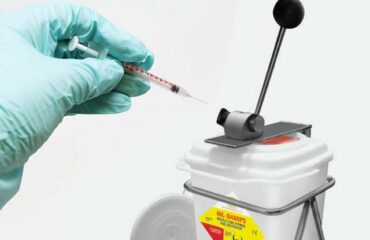
Biomedical waste management has become a crucial issue in India due to the increase in healthcare facilities and the amount of waste generated by them. The proper disposal of biomedical waste is essential to prevent the spread of infections and diseases. It is also crucial in terms of environmental health and the protection of human life.
India generates a significant amount of biomedical waste, which includes sharps, syringes, discarded medicines, expired chemicals, and PPE (personal protective equipment) waste. According to a recent study conducted by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India generates over 500 tonnes of biomedical waste every day. Many of these wastes contain harmful micro-organisms and toxic substances that pose a significant threat to human health and the environment.
The Indian government has taken several measures to address the issue of biomedical waste management. The Biomedical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 1998, were introduced by the Ministry of Environment and Forests to regulate biomedical waste disposal. The rules were revised in 2016, taking into account the latest developments in waste management technology and improving their implementation.
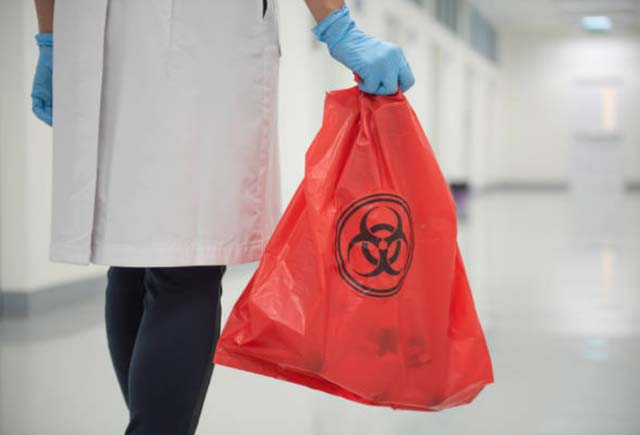
One of the essential aspects of biomedical waste management is the segregation of waste at the source. All healthcare facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and laboratories, are required to segregate and classify their medical waste into various categories as per the guidelines provided by the CPCB. This ensures that waste is disposed of safely according to its risk category.
Once segregated, biomedical waste must be treated and disposed of in a safe and environmentally friendly manner, by following a set of approved modes of treatment and disposal. This includes incineration, shredding & autoclaving, microwave treatment, and chemical treatment, among others. The CPCB has also authorized several agencies, both private and public, to offer disposal and treatment services for biomedical waste.
Despite the steps taken by the Indian government to regulate the disposal of biomedical waste, there is still much work to be done. Several recommended directives will ensure that healthcare providers and the public can comply with the rules in place effectively. They may include improved enforcement mechanisms, better public awareness campaign creation, and a more stringent monitoring of medical facilities to follow the guidelines of handling biomedical waste appropriately.
In conclusion, proper biomedical waste management is essential to control medical infections and diseases, protect human and environmental health, and ensure that our society is a safe and healthy one. It is important for the government, healthcare providers, and the public to work together to ensure that the biomedical waste generated is correctly treated and managed in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner.